

Historically, the second law was an empirical finding that was accepted as an axiom of thermodynamic theory.
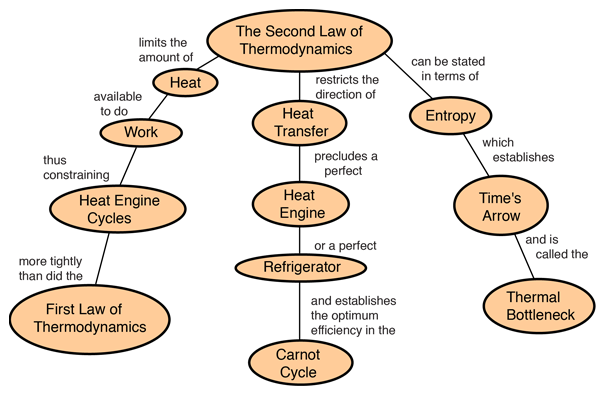
An increase in entropy accounts for the irreversibility of natural processes, often referred to in the concept of the arrow of time. If all processes in the system are reversible, the entropy is constant. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems left to spontaneous evolution cannot decrease, as they always arrive at a state of thermodynamic equilibrium, where the entropy is highest at the given internal energy.

It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law of thermodynamics establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
